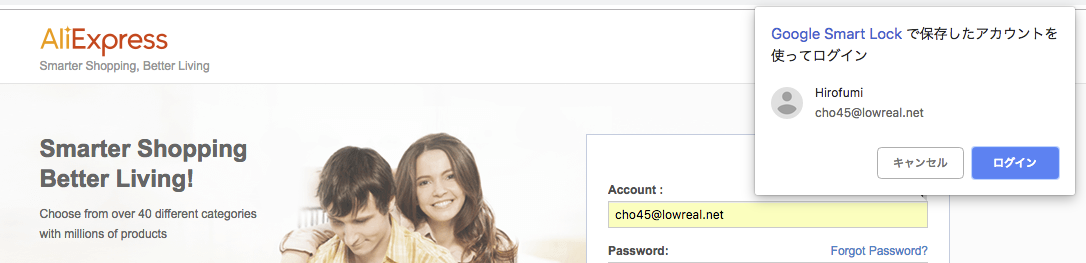
Aliexpress を利用しているとサインイン時に自動的にログインする仕組みが導入されていることに気付く。知らない人のために説明すると、以下のような挙動をする。
- ログインページにいくと「Google Smart Lock で保存したアカウントを使ってログイン」というブラウザのUIが表示される
- そのまま「ログイン」ボタンを押すと自動的にサイトにログインしてページ遷移する
- セッション切れのときに My Orders などにアクセスしようとすると、一度ログインページに遷移した後、自動的にログインして My Orders ページに遷移しなおす (ログイン済みになって見れるようになる)
あまり他のサイトだと見ない挙動なので最初は驚いたけど、便利。
仕組み
これは Credential Management API という仕組みを使うと実現できる。現状では Chrome しか対応していないようだ。Google が公開しているエントリにこれの実現方法も書いてある。https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/06/credential-management-updates 割と詳しい説明が書いてあるのでこれを読めばよろしい。が、自分でも試してみたのでメモしておく。
雑に自分のサイトに自動ログインを導入したい、と思った場合、ログインページに以下のようなコードを仕込むだけで実現できてしまう。
(async function () {
const cred = await navigator.credentials.get({
password: true
});
document.getElementById('username').value = cred.id;
document.getElementById('password').value = cred.password;
document.getElementById('login').submit();
})(); もちろんこれだけだと欠点がある。すなわち、ログインページを表示した際に強制的にログインしてしまう。もしあなたのサイトが認証状態がないときにログインページにリダイレクトして戻ってくるような仕様だとすると「ログアウト」が不可能になってしまいます。この実装だけではダメですね。
これを防ぐにはログアウト時に preventSilentAccess() を使ったり、 get() に指定する mediation の値を変更したりする必要があります。詳しくは前述の Google のエントリを読むと良いでしょう。
コードを見るとわかるが全く複雑なことはないですね。id と password が JavaScript から取得できるため、それを既設のフォームに埋めているだけ。console.log() のコメントアウトをはずすと、自分のパスワードが console に表示されるのでビビることができます。
JSからパスワードとれんの??? こわくない??
こわいわ〜と直感的に思いますね。その感覚は正しいと思うんです。でもね、「ブラウザに保存しているパスワード」は実情、自動フィルインされるわけですが、このフィルインされたパスワードって Credential Management API に関係なく、そもそも input.value で JS から読めるんですよね。
そう考えると、このAPIは単にフィルイン+ログインボタンクリックという操作を、確実かついい感じに(ログアウトも考慮して)行える方法で代行しているだけという仕組みになりますね。複数アカウントを考慮しつつ1クリック減らせるという感じです。
-
トップ
-
tech
-
Chrome で保存したパスワードをウェブサイト側から利用する
![きっと、うまくいく [Blu-ray] - アーミル・カーン](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/517mHuR6jqL._SL500_.jpg)
![帰ってきたヒトラー [Blu-ray] - オリヴァー・マスッチ](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51Dn+wRwBsL._SL500_.jpg)